Silicon Bonding is attaching silicon, a synthetic rubber-like substance, to a metal component. Silicon is renowned for being flexible, strong, and heat resistant. When heated, it can be easily molded into any shape, making it a superior sealant material once dry. Silicon creates an airtight connection when combined with stainless steel or aluminum; as a result, it is less susceptible to corrosion. Additionally, silicon is an inert substance that won’t react chemically or physically with other liquids, solids, or gas. Read More…
RD Rubber Technology is an ISO 9001:2015 certified company that is highly responsive and flexible to customer needs. We can take care of design, development, and prototyping as well as short run, long run, and high volume production. We offer compression, transfer, LIM, and rubber to metal bonding. We also do silicone to thermal plastic bonding.
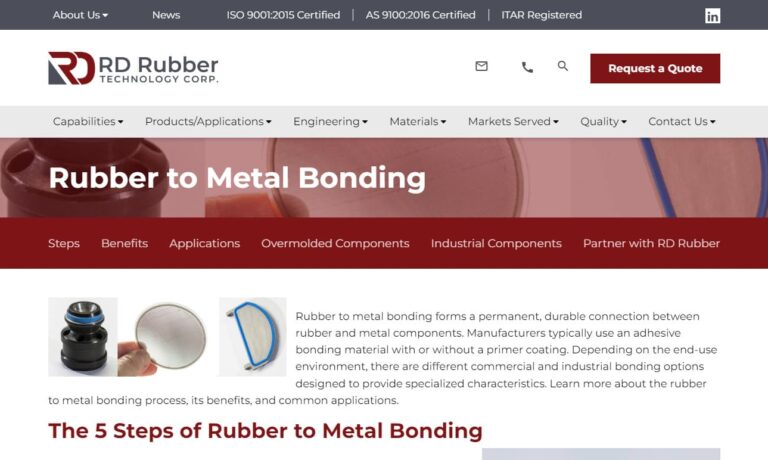
Since 1984 we have been providing excellent high performance solution to our client’s toughest bonded metal to rubber issues. Our skilled teams of engineers and technicians will work closely with you in order to ensure that we are filling your exact requirements on the products that we provide. Allow us to show you the difference when you work with true experienced professionals. Visit our...
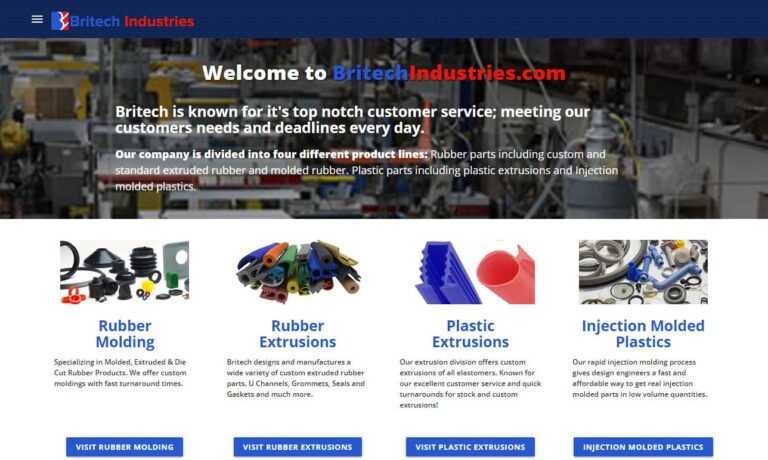
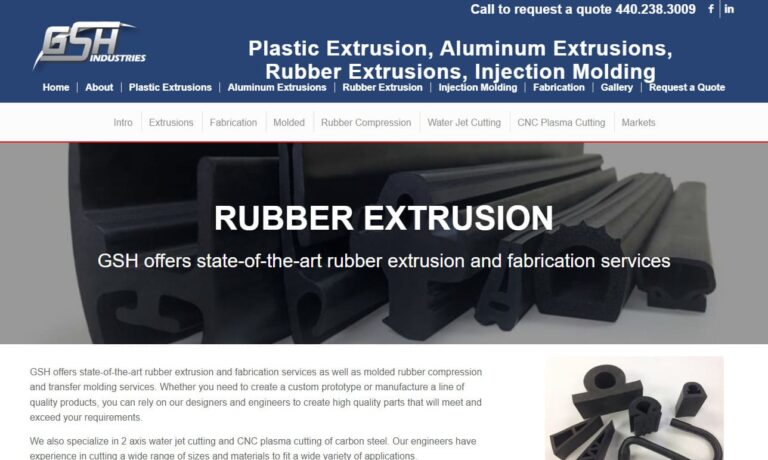
For over 25 years, GSH has provided top quality contract manufacturing services, and we strive to remain on the cutting edge of our industry.
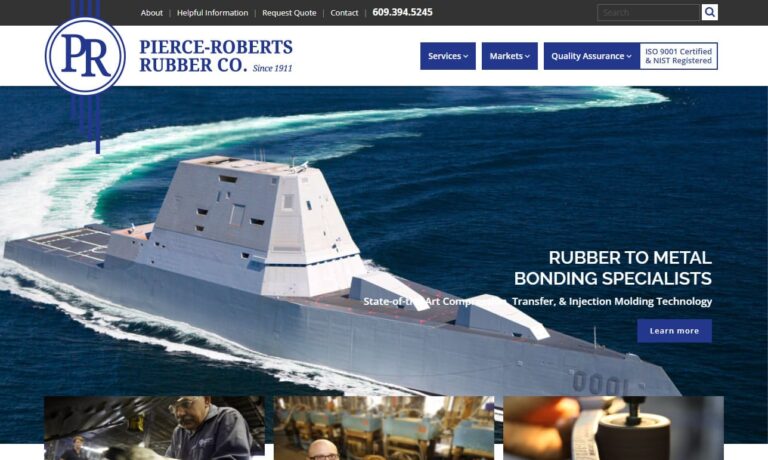
With more than a century of manufacturing experience, Pierce-Roberts Rubber Co. is your source for custom molded rubber products.
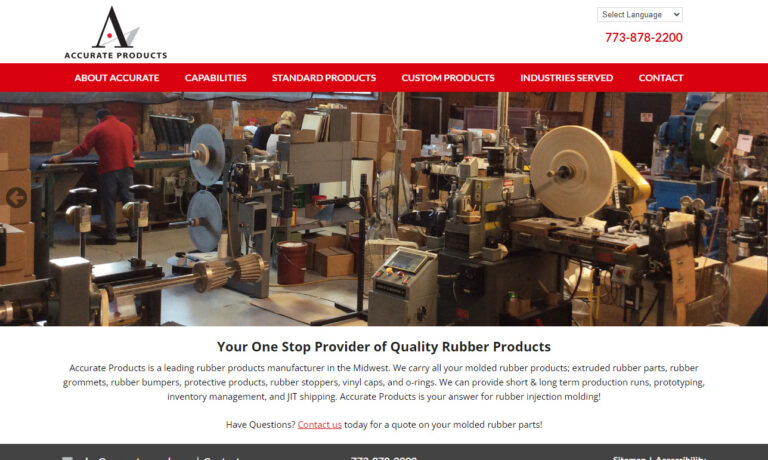
See how Accurate Products can bond natural and synthetic rubber to a wide variety of materials for applications such as tires, gaskets, seals, rolls, hoses, tubes, vibration isolators, shock mounts, electrical components, bumpers, drive wheels, etc.
From molding products made of homogeneous rubber, to rubber bonded to metal as well as other various materials. Mason Rubber makes efficient use of state of the art technology to produce a quality product.

Our economical products are made from high-quality solutions that will last you for many years to come. We are a dependable manufacturer that will work with you every step of the way.

At National Rubber Corp., we specialize in advanced rubber-to-metal bonding solutions designed to meet the demanding requirements of diverse industries. With extensive expertise and precision manufacturing capabilities, we produce durable, high-quality components that seamlessly integrate rubber materials with metal substrates.

Since 1955, Jet Rubber Company, an Employee Owned Company, has been custom molding rubber and rubber-to-metal components for a variety of industries and applications.

More Silicon Bonding Manufacturers
Surface Preparation for Silicon Bonding
Proper surface preparation is a fundamental step in achieving a strong, durable bond between silicone and other substrates such as metals, plastics, or glass. For silicon bonding processes, the substrate should be thoroughly cleaned using isopropanol (isopropyl alcohol). This step is essential to remove processing lubricants, oils, dust, and contaminants that can interfere with adhesive performance and bonding strength. Alternative cleaners, such as methylated spirits or white spirits, are not recommended as they may leave unwanted residues or impart an abrasive texture, which can compromise the integrity of the bond.
After cleaning, always ensure the complete evaporation of the solvent before proceeding. In industrial applications and manufacturing environments, surface preparation may also include abrasion, plasma treatment, or corona discharge to further enhance the wettability and adhesion properties of silicone and the mating substrate. If you’re wondering, “How do I prepare surfaces for silicone bonding in high-performance environments?”, consider integrating these advanced pre-treatment methods based on your specific application needs.
Adhesive Selection for Silicon Bonding Applications
Selecting the right silicone adhesive is critical to the success of your bonding application. Industrial adhesives for silicone bonding must offer high adhesion, flexibility, chemical resistance, and, in certain cases, rapid curing times. Silicone-based adhesives remain the most compatible choice, providing strong bonds with minimal risk of incompatibility. However, for those seeking fast-curing adhesives that avoid isocyanate-based chemistries due to safety or regulatory concerns, the options become more specialized.
Primers play a vital role in enhancing adhesive performance. A basecoat or silicone primer—such as a polyolefin primer—can be applied before the main adhesive layer. These primers condition the silicone surface, improving bonding strength and durability, especially when joining silicone rubber to low-energy surfaces like polyethylene or polypropylene. If you’re evaluating, “Which primer is best for silicone-to-metal or silicone-to-plastic bonding?”, consult adhesive manufacturers for compatibility charts and technical datasheets tailored to your use case.
Types of Adhesives Used for Silicon Bonding
Fluorosilicone Adhesive
Fluorosilicone adhesives are engineered with trifluoropropyl groups, dramatically increasing their chemical resistance compared to standard silicone adhesives. These adhesives withstand exposure to solvents, fuels, oils, acids, and alkalis, making them ideal for demanding industrial sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing. Fluorosilicone sealants excel when bonding silicone to metals, plastics, or composite substrates, maintaining bond integrity in corrosive or high-temperature environments.
Fluorosilicone adhesives are available in both one-part and two-part systems. One-part formulations cure upon exposure to atmospheric moisture, while two-part systems require careful mixing and often offer faster, more predictable curing cycles, which is beneficial in automated production lines. If you’re searching for “high-performance chemical-resistant adhesives for silicone bonding”, fluorosilicone products are a top choice.

Key Features and Industry Applications
- Exceptional resistance to harsh chemicals, fuels, and solvents
- Stable performance in extreme temperatures (cryogenic to elevated heat)
- Ideal for aerospace seals, fuel system components, automotive gaskets, and chemical processing equipment
- Suitable for bonding silicone to metals, plastics, and specialty composites
Pressure-Sensitive Silicone Adhesives (PSAs)
Pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) based on silicone polymers are valued for their ability to form instant bonds with low application pressure. These adhesives utilize synthetic elastomers that provide outstanding heat and temperature resistance, as well as robust adhesion to low surface energy materials. PSAs are commonly supplied on a carrier (such as film or tape) and bond to diverse substrates, including plastics, fabrics, papers, and metals, simply by applying pressure.

Thanks to their unique polymer structure, PSAs can be engineered for a wide range of applications—everything from masking tapes and protective films to medical device assembly and electronic insulation. They are highly resistant to extreme environmental conditions, UV radiation, and moisture, making them a reliable solution in both indoor and outdoor settings. Wondering “How do I choose the right PSA for bonding silicone to plastic, metal, or glass?” Consider your temperature, environmental exposure, and regulatory requirements.
Benefits and Typical Uses
- Immediate bonding without the need for heat or curing
- Excellent conformability to irregular or textured surfaces
- Low outgassing, suitable for electronics, optics, and cleanroom applications
- Widely used for medical tapes, automotive trim, appliance assembly, and graphic films
Room Temperature Vulcanizing Silicone Adhesive (RTV Silicone)
RTV silicone adhesives are one of the most popular choices for both industrial and consumer applications. These adhesives cure at room temperature, forming strong, flexible, and durable bonds that also serve as effective gaskets or seals. RTV silicones are renowned for their outstanding temperature tolerance, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation properties.
Unlike some other silicone adhesives that require prolonged curing times, RTV silicones begin to harden immediately upon exposure to atmospheric moisture, often achieving full cure within 24 hours. This makes them ideal for rapid prototyping, maintenance repairs, and field assembly. They are commonly used in the construction, automotive, electronics, and appliance industries for sealing, bonding, and encapsulating components.

Advantages and Industrial Applications
- High flexibility and elongation, accommodating thermal expansion and vibration
- Maintains seal integrity over a wide temperature range (-60°C to 200°C and beyond)
- Outstanding weatherability and UV resistance for indoor and outdoor use
- Preferred for HVAC gasketing, sealing electrical enclosures, and bonding glass to metal or plastic
- Electrical grade RTVs are used for potting and insulating sensitive electronics
Silicone Rubber Adhesive: Properties and Use Cases
Silicone rubber adhesives combine the resilient properties of silicone elastomers with strong adhesive performance. These adhesives are especially valued in applications requiring water resistance, flexibility, and long-term durability. Their unique formulation prevents decay, cracking, or yellowing, even after prolonged exposure to sunlight, saltwater, or fluctuating temperatures.
Marine applications are a prominent use case—silicone rubber adhesives are regularly employed to seal and waterproof boats, yachts, and other watercraft. The adhesive’s flexibility and waterproof properties protect hulls, joints, and seams from leaks and corrosion. In addition, silicone adhesives for glass bonding are favored in architectural glazing, aquariums, and laboratory equipment where clarity and environmental resistance are paramount.
Explore Related Questions:
- What makes silicone rubber adhesive the best choice for marine sealing?
- How does silicone adhesive compare to polyurethane or epoxy adhesives in outdoor applications?
- Can silicone adhesives be used for high-movement joints or expansion gaps?
Applications and Benefits of Silicon Bonding
Silicon bonding technology finds widespread use across diverse industries, thanks to the inherent properties of silicone and the versatility of modern adhesives. Below are some leading applications and the key benefits that drive selection of silicon bonding solutions:
- Medical Devices and Healthcare: Silicone bonded to metal, plastic, or glass is commonly found in hospitals, operating rooms, and clinics. Medical-grade silicone adhesives enable the production of handles, instruments, and components that are biocompatible, non-reactive, and resistant to contamination. There is no risk of bacterial ingress at the bonded interface, ensuring safety and hygiene.
- Surgical and Diagnostic Equipment: Bonded silicone handles and grips for surgical tools provide ergonomic comfort, chemical resistance, and the ability to withstand repeated autoclave sterilization cycles. This durability is crucial for reusable medical instruments and diagnostic devices.
- Analytical and Laboratory Equipment: Silicon-to-metal bonds are used in blood analysis devices, sample handling equipment, and laboratory automation systems, where chemical inertness and sterilizability are key requirements.
- Seals, Gaskets, and Insulation: Owing to its flexibility, compressibility, and resilience, silicone is widely used as a sealing material in gaskets, O-rings, and insulation pads for automotive, industrial, and HVAC applications.
- Prosthetics and Wearable Technology: Advanced silicone bonding techniques enable the production of prosthetic limbs, orthopedic implants, wearable sensors, and flexible medical devices that must conform to complex anatomical shapes while maintaining hypoallergenic properties.
- Consumer Products and Food-Grade Applications: Silicone’s thermal stability and food-safe chemistry make it ideal for kitchenware, bakeware, ice cube trays, and molds. High-temperature silicone adhesives ensure long-lasting bonds even after repeated cycles in ovens, freezers, or dishwashers.
- Special Effects, Molding, and Prototyping: In the film and entertainment industry, silicone bonding is used to create realistic prosthetics, masks, and molds for special effects. Its flexibility, skin safety, and easy release properties are highly valued by artists and engineers alike.
- Electronics, Automotive, and Aerospace: Silicone adhesives are crucial in encapsulating electronics, potting components, and assembling sensors or connectors exposed to vibration, heat, and moisture. In automotive and aerospace engineering, silicone-to-metal and silicone-to-plastic bonding supports lightweight, durable, and reliable assemblies.
What Are the Main Benefits of Silicon Bonding?
- Superior Temperature Resistance: Silicon bonds maintain strength and flexibility from sub-zero to high temperatures, making them ideal for harsh environments.
- Chemical and UV Resistance: Adhesive bonds are stable against fuels, oils, solvents, acids, alkalis, and sunlight exposure.
- Biocompatibility and Safety: Medical and food-grade silicones are non-toxic, hypoallergenic, and meet FDA or USP standards.
- Waterproof and Weatherproof: Silicone bonds repel moisture, resist mold and mildew, and withstand immersion or outdoor exposure.
- Longevity and Low Maintenance: Silicone adhesives and bonded assemblies are engineered for decades of reliable performance with minimal degradation.
- Versatility Across Materials: Modern formulations enable bonding of silicone to metals, plastics, composites, glass, ceramics, and fabrics.
Decision Factors: How to Choose the Best Silicon Bonding Solution
When selecting a silicon bonding process or adhesive, consider the following factors to ensure optimal results for your specific application:
- Substrate Compatibility: Ensure the adhesive is formulated for the materials you intend to bond (e.g., silicone to metal, silicone to plastic, or silicone to glass).
- Curing Requirements: Do you need a fast room-temperature cure (RTV), a heat-cured bond, or UV-curing for rapid processing?
- Mechanical Stress and Flexibility: Will the bond be exposed to vibration, movement, or thermal cycling? Choose an adhesive with suitable elongation and toughness.
- Chemical and Environmental Exposure: Consider the operating environment—will the bonded assembly encounter chemicals, water, outdoor exposure, sterilization, or extreme temperatures?
- Regulatory and Safety Standards: For medical, food, or electronics applications, select adhesives that comply with necessary safety standards (e.g., FDA, USP Class VI, ISO 10993, UL).
- Application Method: Determine whether the adhesive will be applied manually, via automated dispensing, or as a pre-formed tape or film.
- Cost and Availability: Factor in adhesive price, shelf life, and supply chain considerations, especially for large-scale or mission-critical projects.
Common Questions When Evaluating Silicon Bonding Solutions
- What is the strongest adhesive for bonding silicone to metal or glass?
- How do I ensure long-term durability and environmental resistance?
- Are there food-safe or medical-grade silicone adhesives available?
- Can I automate the adhesive application process for high-volume manufacturing?
- What are the best practices for preparing surfaces before bonding?
Choosing the Right Silicon Bonding Company or Service Provider
Partnering with an experienced silicon bonding company can significantly impact the quality, performance, and cost-effectiveness of your final product. To make the most informed decision, compare at least four to five service providers using our silicon bonding directory. Every company profile highlights key areas of expertise, certifications, material capabilities, and project experience, allowing you to identify partners that best match your requirements.
For a more streamlined vendor selection process:
- Review each silicon bonding company’s capabilities through our website previewer tool, focusing on their experience in your specific industry (e.g., medical, automotive, aerospace, electronics, marine, or consumer products).
- Use our simple RFQ (Request for Quote) form to contact multiple silicon bonding providers simultaneously. Clearly outline your technical requirements, desired performance specifications, and project deadlines to receive accurate, competitive quotes.
- Ask potential partners about their process controls, quality assurance systems, and track record for delivering on time and within budget.
- Request case studies or references from similar projects to gain confidence in their ability to handle your unique bonding challenges.
Key Considerations When Selecting a Silicon Bonding Company
- Technical expertise in bonding silicone to various substrates
- Experience with regulatory and safety compliance for your industry
- Availability of advanced testing, inspection, and quality control capabilities
- Capacity for small-batch prototyping as well as high-volume production
- Responsiveness and support throughout the project lifecycle
Maximize Your Project Success with Expert Silicon Bonding Services
Whether you’re developing a new medical device, upgrading industrial equipment, or designing consumer products, the right silicon bonding solution can make all the difference. Contact trusted providers, review technical documentation, and request samples or prototypes to validate adhesive selection and process reliability. If you have unique application challenges—such as bonding dissimilar materials, meeting strict sterilization protocols, or achieving high-throughput manufacturing—leverage our resources and expert network to find the best-fit partner for your needs.
Ready to get started? Search our silicon bonding company directory or request a quote today to connect with leading experts and unlock the full potential of advanced silicone bonding technology for your next project.







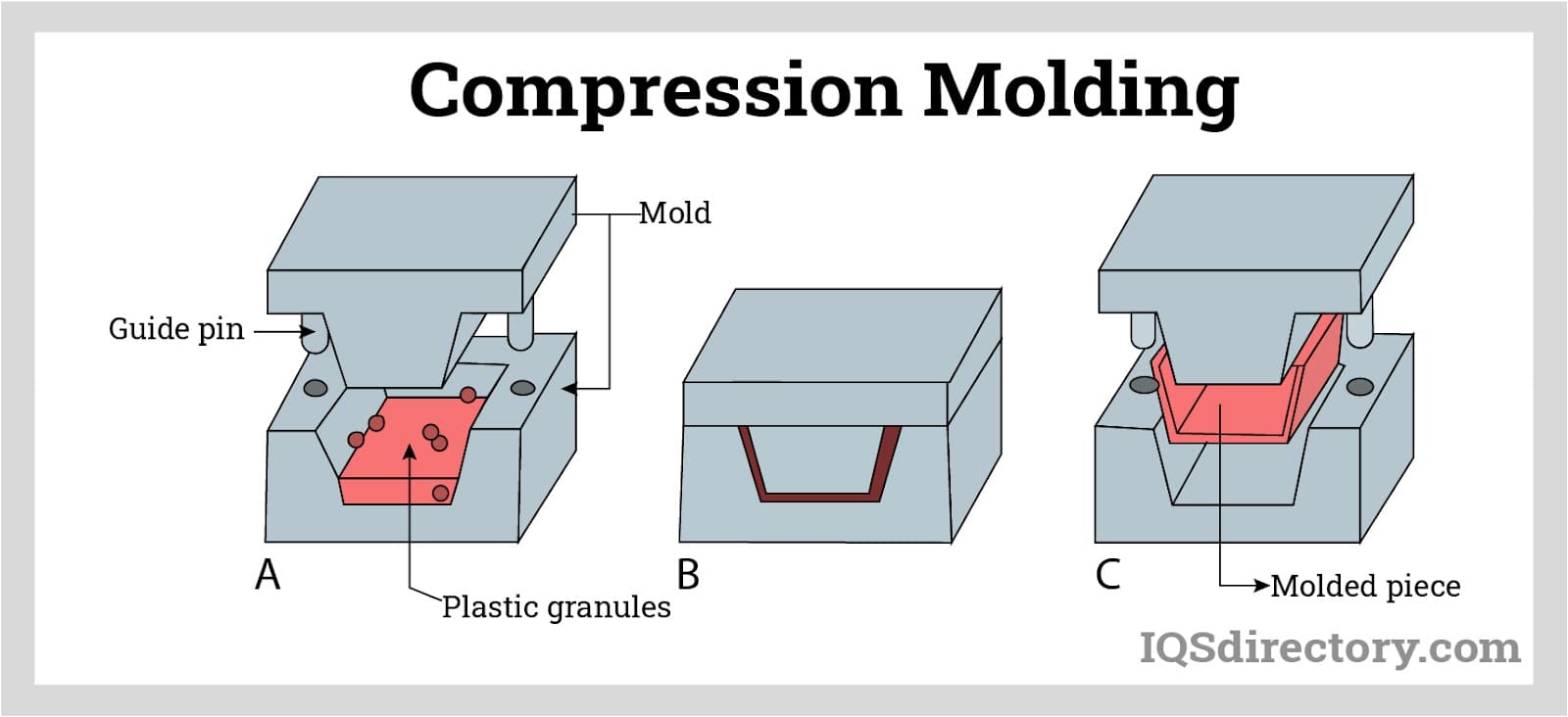
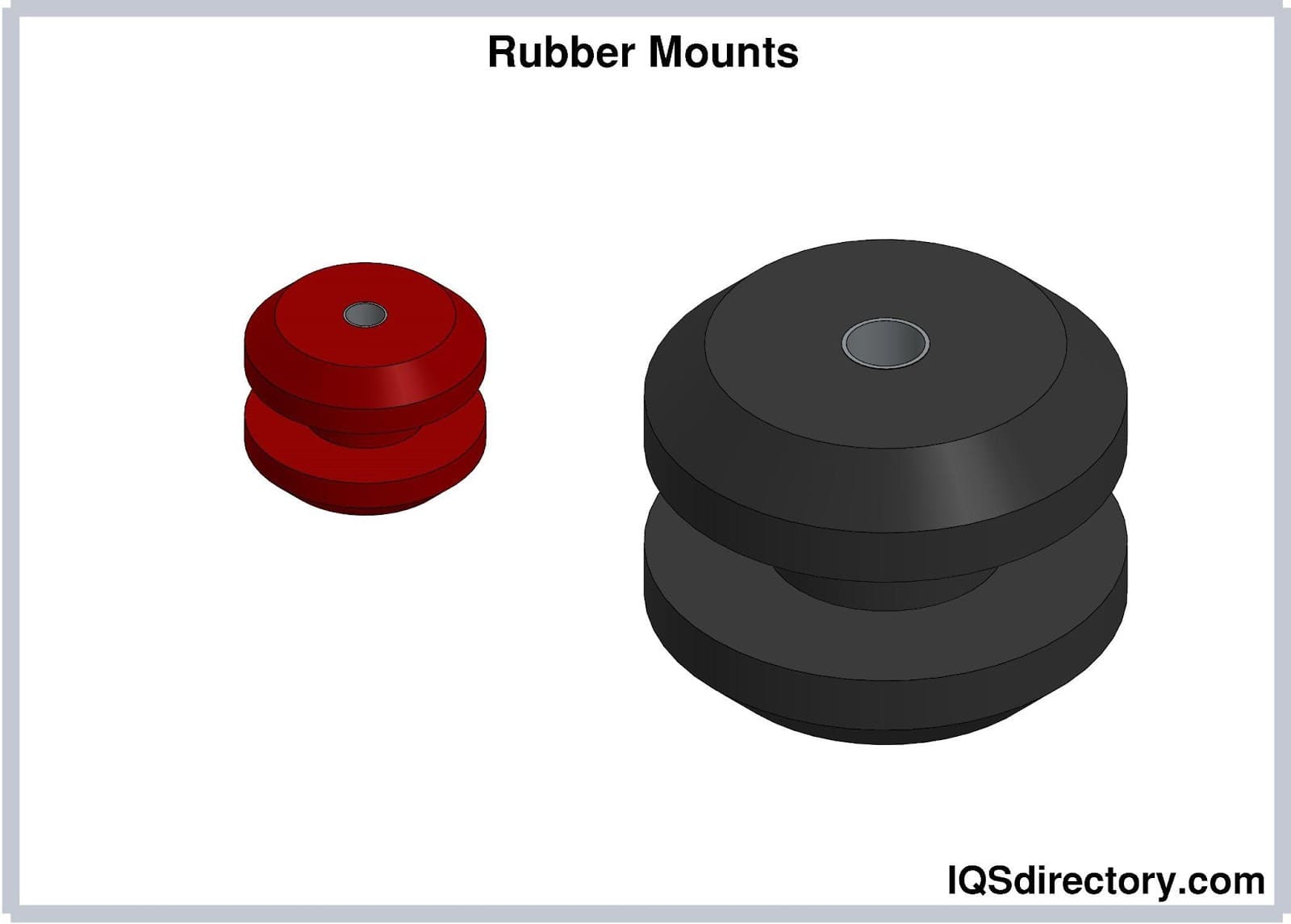


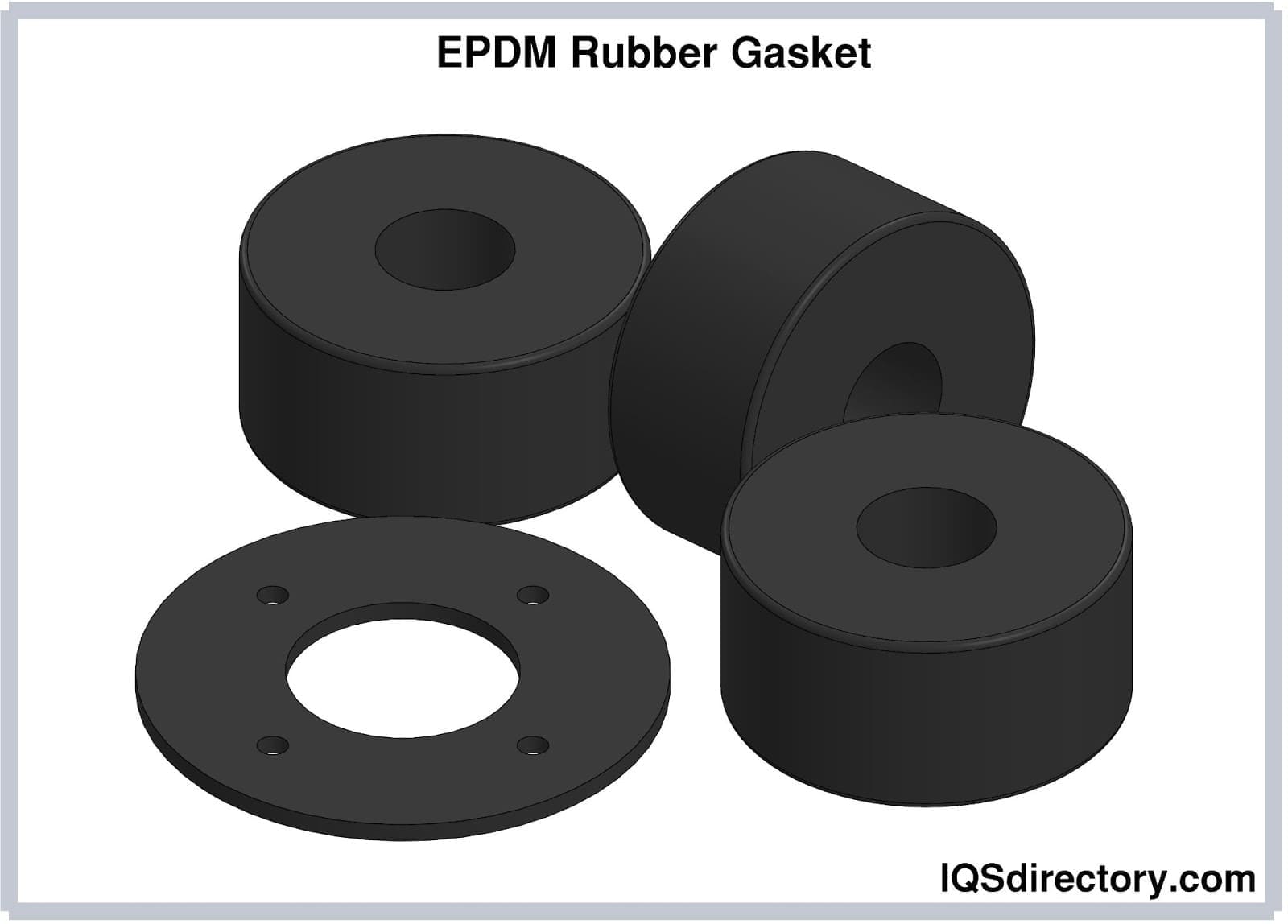
 Rubber Extrusions
Rubber Extrusions Rubber Molding
Rubber Molding Rubber to Metal Bonding
Rubber to Metal Bonding Rubber Tubing
Rubber Tubing Vibration Absorbers
Vibration Absorbers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services