Rubber bonding is joining two pieces of rubber or rubber and another substance, such as metal, wood, or plastic. One can either use hot rubber bonding or cold rubber bonding. Although both have benefits, a hot rubber bond is typically stronger than a cold bond. However, hot rubber bonding is a more expensive procedure requiring more setup and labor, raising a product’s cost. Choosing the right procedure depends on the application of the final product. Read More…
RD Rubber Technology is an ISO 9001:2015 certified company that is highly responsive and flexible to customer needs. We can take care of design, development, and prototyping as well as short run, long run, and high volume production. We offer compression, transfer, LIM, and rubber to metal bonding. We also do silicone to thermal plastic bonding.
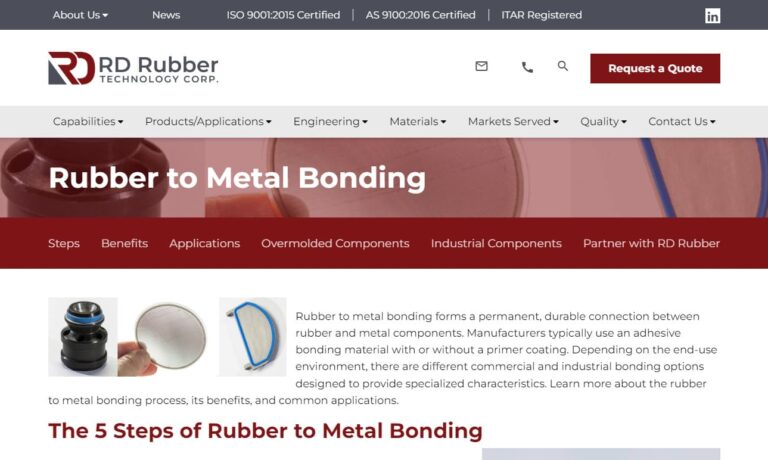
Since 1984 we have been providing excellent high performance solution to our client’s toughest bonded metal to rubber issues. Our skilled teams of engineers and technicians will work closely with you in order to ensure that we are filling your exact requirements on the products that we provide. Allow us to show you the difference when you work with true experienced professionals. Visit our...
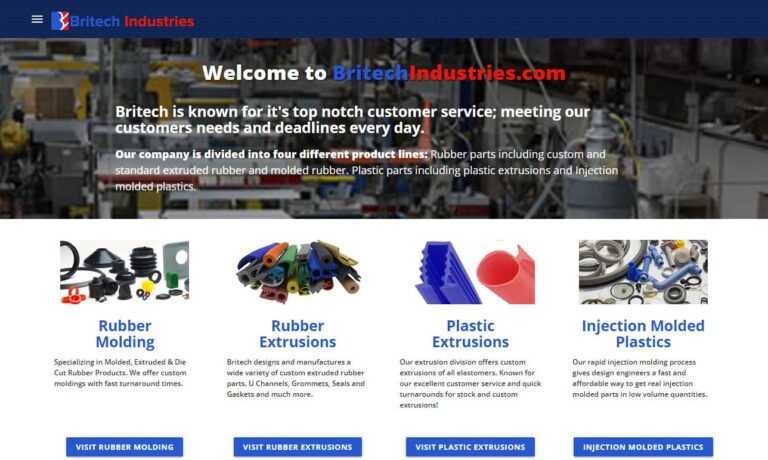
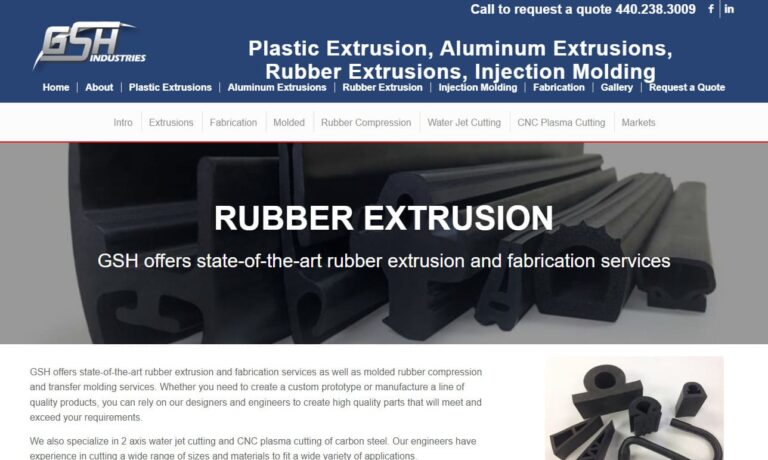
For over 25 years, GSH has provided top quality contract manufacturing services, and we strive to remain on the cutting edge of our industry.
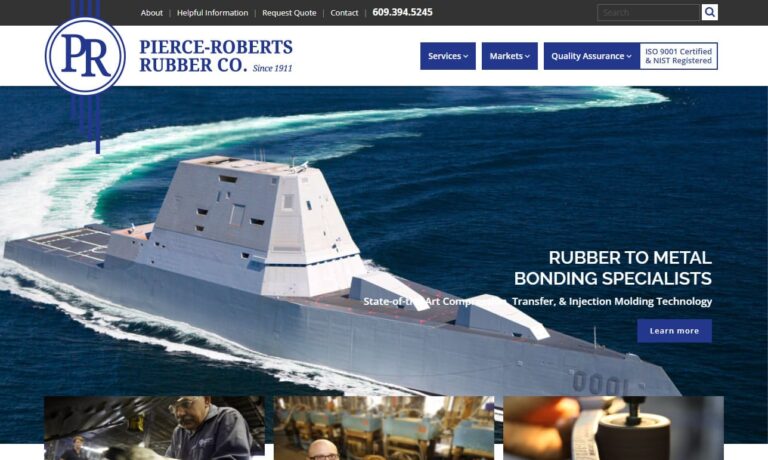
With more than a century of manufacturing experience, Pierce-Roberts Rubber Co. is your source for custom molded rubber products.
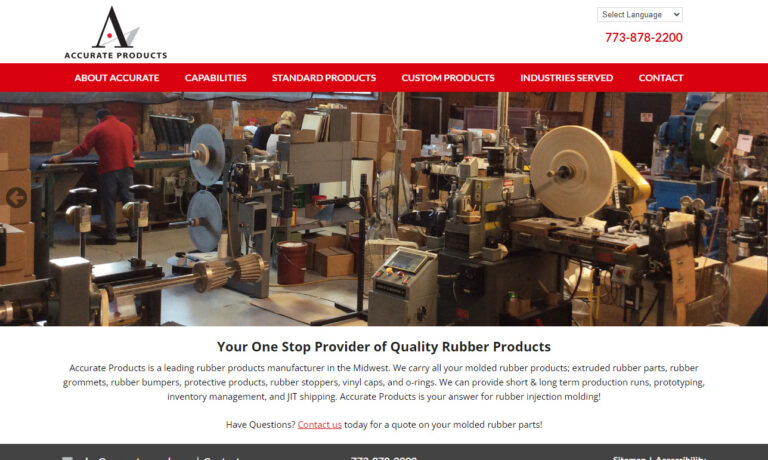
See how Accurate Products can bond natural and synthetic rubber to a wide variety of materials for applications such as tires, gaskets, seals, rolls, hoses, tubes, vibration isolators, shock mounts, electrical components, bumpers, drive wheels, etc.
From molding products made of homogeneous rubber, to rubber bonded to metal as well as other various materials. Mason Rubber makes efficient use of state of the art technology to produce a quality product.

Our economical products are made from high-quality solutions that will last you for many years to come. We are a dependable manufacturer that will work with you every step of the way.

At National Rubber Corp., we specialize in advanced rubber-to-metal bonding solutions designed to meet the demanding requirements of diverse industries. With extensive expertise and precision manufacturing capabilities, we produce durable, high-quality components that seamlessly integrate rubber materials with metal substrates.

Since 1955, Jet Rubber Company, an Employee Owned Company, has been custom molding rubber and rubber-to-metal components for a variety of industries and applications.

More Rubber Bonding Manufacturers

What to Consider When Choosing an Adhesive for Rubber Bonding
When it comes to rubber bonding, selecting the right adhesive is crucial for achieving optimal performance, long-term durability, and a reliable bond. Different types of rubber—whether natural or synthetic—possess unique physical, chemical, thermal, and electrical properties. As a result, the adhesive solutions required for effective bonding can vary significantly depending on your specific application and the substrates involved. For example, bonding rubber to metal, plastic, glass, ceramics, or even other rubbers each presents its own set of challenges.
Industrial manufacturers, product engineers, and hobbyists alike must carefully evaluate these factors when searching for the best rubber adhesives or rubber bonding agents. Whether you’re working on automotive components, industrial rollers, gaskets, footwear, or consumer products, the right adhesive can mean the difference between success and failure.
Fortunately, a wide variety of rubber adhesives are available, including one-part and two-part adhesives, cyanoacrylates, epoxies, structural acrylics, polyurethane adhesives, and silicone-based solutions. Selecting the best adhesive for your specific rubber bonding project requires understanding both the material properties and the end-use requirements.

The Properties of a Perfect Rubber Adhesive
Are you wondering how to choose the best adhesive for bonding rubber? The ideal rubber bonding adhesive must meet several key criteria to ensure a robust, flexible, and durable bond. These properties impact not only the immediate adhesion but also the long-term resilience and performance of the bonded assembly under real-world conditions.
Versatility
While many all-purpose glues and general adhesives can bond various materials, their performance on rubber is often inferior to that of specialty rubber adhesives. Specialty adhesives are engineered to address the unique surface energy, porosity, and flexibility of rubber materials. For example, hot melt adhesives and contact adhesives may provide a quick and effective way to bond rubber to metal, wood, or plastics. In addition, certain adhesives excel at joining specific types of rubber, such as latex, EPDM, NBR (nitrile), SBR (styrene butadiene), or silicone rubber.
Pro Tip: If you’re asking, “What is the best adhesive for joining rubber to plastic or metal?” or “Can I use super glue on rubber?” explore our detailed guides on bonding rubber to metal and bonding rubber to plastic for expert recommendations.
Adhesion
The adhesive’s ability to create a strong, lasting bond is paramount. Because most rubber parts, such as rubber hoses, automotive seals, vibration mounts, conveyor belts, and shoe soles, require flexibility, the chosen adhesive must be able to bend and stretch without cracking or losing adhesion. Look for adhesives specifically labeled as “flexible bonding” or “rubber-to-substrate adhesives.” Many rubber products rely on adhesives that maintain strength under dynamic loads, repeated flexing, and environmental exposure.
Curing Time
Application efficiency often depends on the adhesive’s curing speed. For high-volume production or field repairs, fast-setting adhesives like cyanoacrylates (“super glues”) or instant-bonding acrylics may be preferred. However, for structural applications requiring maximum strength, a longer curing period—such as with two-component epoxy adhesives—can yield a stronger final bond. Always refer to the manufacturer’s technical data sheet (TDS) for details on open time, set time, and full cure.
Elasticity
The application’s requirements will dictate how flexible or elastic the adhesive must remain after curing. For instance, the sulfur content in vulcanized rubber adhesives impacts elasticity—higher sulfur levels reduce flexibility but may increase strength and chemical resistance. For products subject to ongoing movement, such as gaskets, diaphragms, or vibration dampers, high elasticity is critical to prevent bond failure.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
In many industrial rubber bonding applications, the adhesive must withstand exposure to heat, moisture, UV light, chemicals, oils, and solvents. Weather-resistant or chemical-resistant adhesives—such as specialized silicone rubber adhesives—can protect bonds in demanding environments. Always evaluate the expected service conditions and select an adhesive accordingly.
The Different Types of Rubber Adhesives
Still wondering, “What are the different types of adhesives for rubber bonding?” Here’s a closer look at the main categories of rubber adhesives and their best-use scenarios:
Silicone Rubber Adhesives
Silicone-based adhesives are often the top choice for high flexibility and extreme temperature resistance. These adhesives remain elastic after curing and are renowned for their resistance to heat, moisture, UV radiation, and a variety of chemicals. Typical applications include bonding silicone rubber gaskets, medical devices, kitchenware, and electrical insulation. Their non-corrosive nature makes them ideal for electronics and sensitive assemblies.
- Excellent for high-temperature or outdoor applications
- Great for bonding EPDM, silicone, and fluorosilicone rubbers
- Often used in HVAC, automotive, and appliance manufacturing
Structural Acrylic Rubber Adhesives
Structural acrylic adhesives offer a balance of strength and flexibility, making them suitable for rubber-to-metal and rubber-to-plastic bonding where high shear and peel strength are essential. Two-part systems provide a long shelf life and allow for precise mixing ratios, which is why they are frequently used in industrial assembly, aerospace, and transportation sectors.
- Fast curing, yet strong and durable
- Often used for automotive rubber mounts, seals, and bushings
- Good resistance to environmental stress and vibration
Epoxy Adhesives
Epoxy adhesives excel in applications requiring superior strength and structural integrity. Two-part epoxies are especially effective for bonding rubber to metal, glass, or ceramics, but they are less flexible than silicone or polyurethane adhesives. Epoxies are commonly used in industrial machinery, electronics, and repair work.
- Exceptional chemical and heat resistance
- Ideal for structural bonding and load-bearing applications
- Excellent adhesion to a wide range of substrates
Cyanoacrylate Rubber Adhesives
Cyanoacrylate adhesives, often known as “super glue,” are renowned for their instant bonding capability. These fast-acting adhesives are suitable for many general-purpose rubber bonding tasks and can bond rubber to plastic, metal, or other rubbers. However, their cured bond is rigid; thus, they are not recommended for joints subject to ongoing flexing or movement.
- Best for small repairs and quick fixes
- Moisture-activated for rapid curing
- Limited flexibility—avoid for applications requiring bonded parts to flex
Polyurethane Rubber Adhesives
Polyurethane adhesives are highly regarded for their combination of flexibility, toughness, and environmental resistance. They work well for bonding rubber to porous and non-porous substrates, making them suitable for automotive, footwear, and construction industries.
- Resistant to abrasion, impact, and environmental exposure
- Excellent adhesion to leather, rubber, wood, and concrete
- Available in one-part and two-part formulations
Common Applications and Use Cases for Rubber Bonding
Looking for real-world applications of rubber adhesives? Here are some popular use cases where high-performance rubber bonding is essential:
- Automotive industry: Bonding weatherstripping, gaskets, vibration dampers, bumpers, and seals
- Electronics and electrical: Sealing components, insulating wires, and bonding flexible circuits
- Construction: Installing flooring, anti-slip mats, and expansion joints
- Medical devices: Assembly of medical tubing, wearable devices, and flexible enclosures
- Footwear and apparel: Attaching soles, midsoles, and decorative rubber components
- Consumer goods: Creating waterproof seals for containers, toys, and sports equipment
- Industrial machinery: Mounting vibration pads, grommets, conveyor belts, and rollers
Each application may have unique requirements for adhesive type, curing time, flexibility, and resistance. Understanding these needs helps in selecting the most appropriate rubber bonding adhesive for your project.
A Step-by-Step Guide for Gluing Rubber
Are you searching for “How do I glue rubber to metal, plastic, or another substrate?” Follow this comprehensive guide to achieve a professional-grade bond, whether you’re in a production environment or tackling a DIY project.
1. Preparation
Proper surface preparation is the foundation of a successful rubber bonding process. Begin by identifying the types of materials to be joined—natural rubber, synthetic rubber (such as EPDM, NBR, or SBR), and the substrate (metal, plastic, wood, etc.). The ideal rubber adhesive should match the composition of the materials for maximum compatibility.
- Thoroughly clean both surfaces to remove contaminants such as dust, oil, grease, or release agents.
- Roughen smooth or glossy surfaces using fine-grit sandpaper to improve mechanical adhesion.
- Wipe surfaces with isopropyl alcohol or a manufacturer-recommended solvent to remove residues.
- For challenging surfaces, apply a primer designed for rubber bonding to enhance adhesion.
Did you know? Many adhesive failures are due to inadequate surface preparation. Investing time in this step can significantly boost bond strength and longevity.
2. Adhesive Application
Once prepared, apply the rubber adhesive in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. The choice of application tool (brush, spatula, roller, or dispenser) may depend on the adhesive’s viscosity and the size of the bonding area.
- Apply adhesive evenly in a thin, consistent layer to one or both surfaces, as specified.
- Ensure good ventilation, especially when working with solvent-based adhesives.
- Pay attention to flash-off time—the period required for solvents to evaporate before joining the parts.
- Press the two surfaces together firmly and maintain pressure for the recommended duration to set the bond.

3. Curing
The final bond strength of your rubber adhesive depends on proper curing. Refer to the product’s technical data for curing times, which can range from a few minutes (for cyanoacrylates) to 24 hours or more (for epoxies and structural acrylics).
- Maintain the bonded assembly under suitable pressure and environmental conditions (temperature, humidity) until the adhesive is fully cured.
- Do not stress, move, or mechanically process the assembly until full cure is achieved to avoid weakening the bond.
- For large assemblies or industrial applications, consider using clamps or jigs to ensure consistent pressure.
Tip: The bonded parts may undergo additional processing, such as trimming, machining, or finishing, after the adhesive has reached its maximum strength.
How to Choose the Right Rubber Bonding Company
If you’re looking for a rubber bonding service provider or a custom rubber bonding manufacturer, making the right choice is crucial for your project’s success. Here are key factors to consider when evaluating rubber bonding companies:
- Assess the company’s technical expertise and experience with your specific material combinations and applications.
- Review their quality certifications (such as ISO 9001, IATF 16949, or AS9100) to ensure compliance with industry standards.
- Evaluate their range of services—do they offer prototyping, custom formulation, surface preparation, and post-bonding testing?
- Request case studies or references from similar projects.
- Examine their production capacity and lead times to meet your requirements.
- Check for value-added services such as design support, inventory management, or supply chain integration.
To ensure you secure the most reliable and cost-effective solution, we recommend comparing at least four to five companies using our rubber bonding directory. Each rubber bonding company features a business profile highlighting their capabilities, experience, and industry focus. Use the integrated contact form to request more information or obtain a quote tailored to your needs.
Want to quickly evaluate multiple providers? Use our website previewer to review company websites, then submit your project details through our simple RFQ form and reach out to several rubber bonding specialists at once. This streamlined approach saves you time while helping you identify the best partner for your application.
Frequently Asked Questions About Rubber Bonding
Curious about rubber bonding adhesives and their applications? Explore these common questions from industrial buyers, engineers, and DIY enthusiasts:
- What is the strongest adhesive for bonding rubber to metal?
Structural acrylics and two-part epoxies are generally considered the strongest for high-stress, load-bearing applications. Surface preparation and adhesive selection are both crucial for maximum strength. - Which adhesive is best for flexible rubber parts?
Silicone and polyurethane adhesives offer the best flexibility and elasticity for continuous movement or vibration. - Can I bond rubber to glass or ceramics?
Yes, specialized epoxies and certain silicone adhesives can reliably bond rubber to glass or ceramic substrates. - How do I repair a torn rubber seal or gasket?
Clean and roughen the damaged area, use a high-quality flexible adhesive, and allow full curing before use. - Where can I buy industrial-grade rubber adhesives?
Visit our rubber adhesives page for a curated selection of top manufacturers and distributors. - How do I compare adhesive products for my project?
Research product datasheets, consult with adhesive manufacturers, and request samples for testing in your application.
Learn More About Rubber Bonding Solutions
Need more guidance on selecting the right adhesive or custom rubber bonding solution for your project? Explore our in-depth resources, product catalogs, and directory of rubber bonding companies to find trusted partners and innovative solutions. Whether you’re researching rubber-to-metal bonding, rubber-to-plastic adhesives, or industrial bonding services, our expertise can help you make informed, confident decisions.
Take the next step: Request a quote from leading rubber bonding specialists, or contact us for personalized recommendations. Let us help you achieve high-performance, cost-effective, and durable rubber bonds for any industry or application.









 Rubber Extrusions
Rubber Extrusions Rubber Molding
Rubber Molding Rubber to Metal Bonding
Rubber to Metal Bonding Rubber Tubing
Rubber Tubing Vibration Absorbers
Vibration Absorbers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services