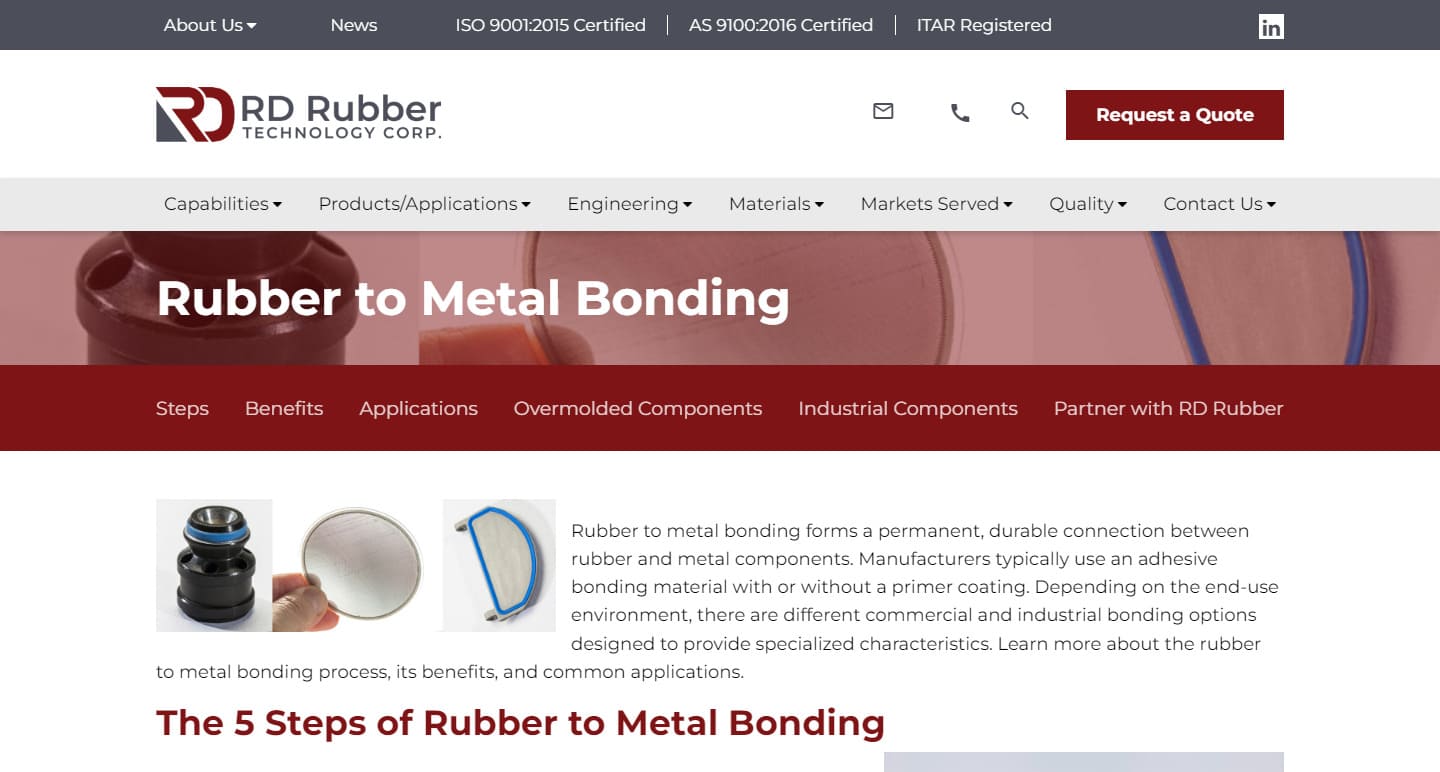
Rubber-to-metal bonding is a great option for items that need metal stability but rubber’s flexibility. Rubber becomes incredibly strong and long-lasting when linked to metal. These properties are crucial in situations with noise, vibration, and harshness. Rubber-to-metal bonding creates dependable, personalised isolators for machinery. Manufacturers have the flexibility to choose the elastomer and metals to be bonded. Each material has unique qualities, such as temperature resistance, robustness, and more. Read More…
RD Rubber Technology is an ISO 9001:2015 certified company that is highly responsive and flexible to customer needs. We can take care of design, development, and prototyping as well as short run, long run, and high volume production. We offer compression, transfer, LIM, and rubber to metal bonding. We also do silicone to thermal plastic bonding.
Since 1984 we have been providing excellent high performance solution to our client’s toughest bonded metal to rubber issues. Our skilled teams of engineers and technicians will work closely with you in order to ensure that we are filling your exact requirements on the products that we provide. Allow us to show you the difference when you work with true experienced professionals. Visit our...
For over 25 years, GSH has provided top quality contract manufacturing services, and we strive to remain on the cutting edge of our industry.
With more than a century of manufacturing experience, Pierce-Roberts Rubber Co. is your source for custom molded rubber products.
See how Accurate Products can bond natural and synthetic rubber to a wide variety of materials for applications such as tires, gaskets, seals, rolls, hoses, tubes, vibration isolators, shock mounts, electrical components, bumpers, drive wheels, etc.
From molding products made of homogeneous rubber, to rubber bonded to metal as well as other various materials. Mason Rubber makes efficient use of state of the art technology to produce a quality product.

Our economical products are made from high-quality solutions that will last you for many years to come. We are a dependable manufacturer that will work with you every step of the way.

At National Rubber Corp., we specialize in advanced rubber-to-metal bonding solutions designed to meet the demanding requirements of diverse industries. With extensive expertise and precision manufacturing capabilities, we produce durable, high-quality components that seamlessly integrate rubber materials with metal substrates.

Since 1955, Jet Rubber Company, an Employee Owned Company, has been custom molding rubber and rubber-to-metal components for a variety of industries and applications.

More Bonding Rubber to Metal Manufacturers

Comprehensive Guide to Rubber to Metal Bonding: Processes, Applications, and How to Choose the Best Manufacturer
Rubber to metal bonding is a specialized process that plays a critical role in the manufacturing of high-performance components for a vast array of industries, including automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, electronics, medical devices, and consumer goods. By securely attaching rubber to metal inserts during the molding process—typically using heat-activated adhesives—manufacturers are able to combine the flexibility and sealing properties of elastomers with the strength, durability, and structural integrity of metals. In many instances, the resulting chemical or mechanical bond between rubber and metal is stronger than the elastomeric material itself, ensuring long-lasting and reliable performance in demanding environments.
What Is Rubber to Metal Bonding?
Rubber to metal bonding, sometimes called rubber-metal adhesion or rubber bonding, is a process in which an elastomer is chemically or mechanically joined to a metal substrate. This is achieved through various molding techniques, such as injection molding, transfer molding, compression molding, and over-molding. The result is a finished part where the rubber is permanently adhered to the metal, creating a composite structure that leverages the advantages of both materials.
Are you wondering how rubber to metal bonding works or which materials are best suited for your application? Keep reading for a detailed breakdown of the process, materials, benefits, and key decision factors when selecting a rubber to metal bonding company.
Different Rubber and Metals That Can Be Bonded
Rubber to metal bonding is a versatile manufacturing process that supports a wide range of elastomeric materials and metal substrates. Selecting the right combination is essential for meeting specific performance, durability, and environmental requirements.
Common Elastomers Used in Rubber to Metal Bonding
- Natural Rubber (NR): Offers excellent elasticity and resilience, making it ideal for vibration isolation, shock absorption, and dynamic sealing.
- Nitrile Rubber (NBR): Known for superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, widely used in automotive and industrial applications.
- Fluoroelastomer (FKM, e.g., Viton™): High resistance to heat, chemicals, and aggressive fluids; used in aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing.
- Ethylene-Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM): Excellent weather, ozone, and water resistance; common in HVAC, automotive, and construction industries.
- Neoprene (CR): Good balance of flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability; used in gaskets, mounts, and seals.
- Silicone Rubber: Exceptional flexibility, temperature stability, and electrical insulation; selected for medical devices, electronics, and food-grade applications. Learn more about silicone bonding.
- Other specialty elastomers: Polyurethane, butyl, and SBR for unique performance requirements.
Metals Suitable for Rubber Bonding
- Steel (Carbon, Stainless, Alloy): Offers strength, rigidity, and corrosion resistance; widely used for structural parts, engine mounts, and industrial couplings.
- Aluminum: Lightweight, cost-effective, and corrosion-resistant; ideal for aerospace, automotive, and lightweight assemblies.
- Brass: Used for electrical, plumbing, and decorative components due to its machinability and corrosion resistance.
- Copper: Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity; used in electronics, connectors, and heat exchangers.
- Beryllium and specialty alloys: Applied in aerospace and electronics for critical tolerance and unique properties.
- Custom and plated metals: Plating or surface treatments (nickel, zinc, chrome) enhance bonding or environmental resistance.
Manufacturers select the elastomer and metal based on factors such as chemical compatibility, operating environment, mechanical stresses, vibration isolation needs, and regulatory requirements.
Rubber to Metal Bonding Process: Step-by-Step Overview
The process of bonding rubber to metal involves several critical steps to ensure optimal adhesion, durability, and product performance. Below is a comprehensive overview of the typical workflow:
-
Surface Preparation:
- Metals are thoroughly cleaned—often using degreasing equipment, grit blasting, or chemical treatments—to remove oils, dirt, oxides, or other contaminants.
- Proper surface preparation is vital for achieving maximum adhesive strength and long-term durability.
-
Primer and Adhesive Application:
- A heat-activated adhesive or primer is uniformly sprayed or brushed onto the prepared metal surface.
- This adhesive forms a chemical bridge between the metal and the elastomer during molding.
-
Placement in Mold:
- The treated metal inserts are accurately positioned within the mold cavities—often using magnets or chaplet pins—to ensure proper alignment and encapsulation.
-
Molding and Curing:
- Rubber is introduced via injection, transfer, or compression molding.
- Heat and pressure activate the adhesive, vulcanize the elastomer, and create a permanent molecular bond.
-
Demolding and Post-Processing:
- The finished bonded parts are removed, inspected, and may undergo trimming or finishing operations to meet final specifications.
-
Testing and Quality Assurance:
- Products are tested for bond strength, adhesion, dimensional accuracy, and performance in simulated operating conditions.
Interested in seeing a video demonstration or detailed case studies of the rubber to metal bonding process? Contact us for additional resources.
Rubber to Metal Bonding Methods: Comparing Key Techniques
There are several primary methods for bonding rubber to metal, each designed to meet specific design, volume, and performance requirements. Understanding these methods is crucial for selecting the right process for your project.
Encapsulation (Insert Moulding)
Encapsulation, also known as insert molding, involves placing a metal insert into the mold before the rubber is added. The elastomer then flows around the metal insert, fully or partially encapsulating it within the finished component. This technique results in a robust mechanical and chemical bond, often with hidden or flush metal surfaces. Encapsulation is commonly used in producing o-rings with embedded wiring, bushings, vibration mounts, and custom seals.
Over-Molding
Over-molding is a process where rubber is molded directly onto a metal substrate, allowing both materials to remain visible in the final product. Over-molding is ideal for applications requiring multiple layers or unique combinations of rubber and metal properties. Common over-molded components include engine mounts, noise/vibration dampers, gaskets, and seals. This method enables complex geometries, improved ergonomics, and enhanced performance characteristics.
Transfer Molding
Transfer molding is a hybrid technique where metal inserts are manually loaded into a heated mold. The elastomer is then introduced into a chamber (pot) and transferred under pressure through channels (runners and sprues) to encapsulate the inserts. The heat and pressure cure the rubber, forming a strong molecular bond to the metal. Transfer molding is favored for its cost-effective tooling, suitability for intricate or multi-cavity parts, and reduced flash compared to compression molding. It is frequently used for grommets, bushings, electrical insulators, and precision-engineered components.

Injection Molding
Injection molding, a high-volume and highly automated process, involves injecting liquid or preheated elastomer into a closed mold containing the metal insert. The mold is subjected to high temperature and pressure, activating the adhesive and vulcanizing the elastomer. Injection molding is ideal for producing large quantities of complex, high-precision bonded parts—such as automotive bushings, suspension components, vibration isolators, and medical device housings. The process delivers consistent quality, tight tolerances, and reduced cycle times, making it the preferred choice for mass production.

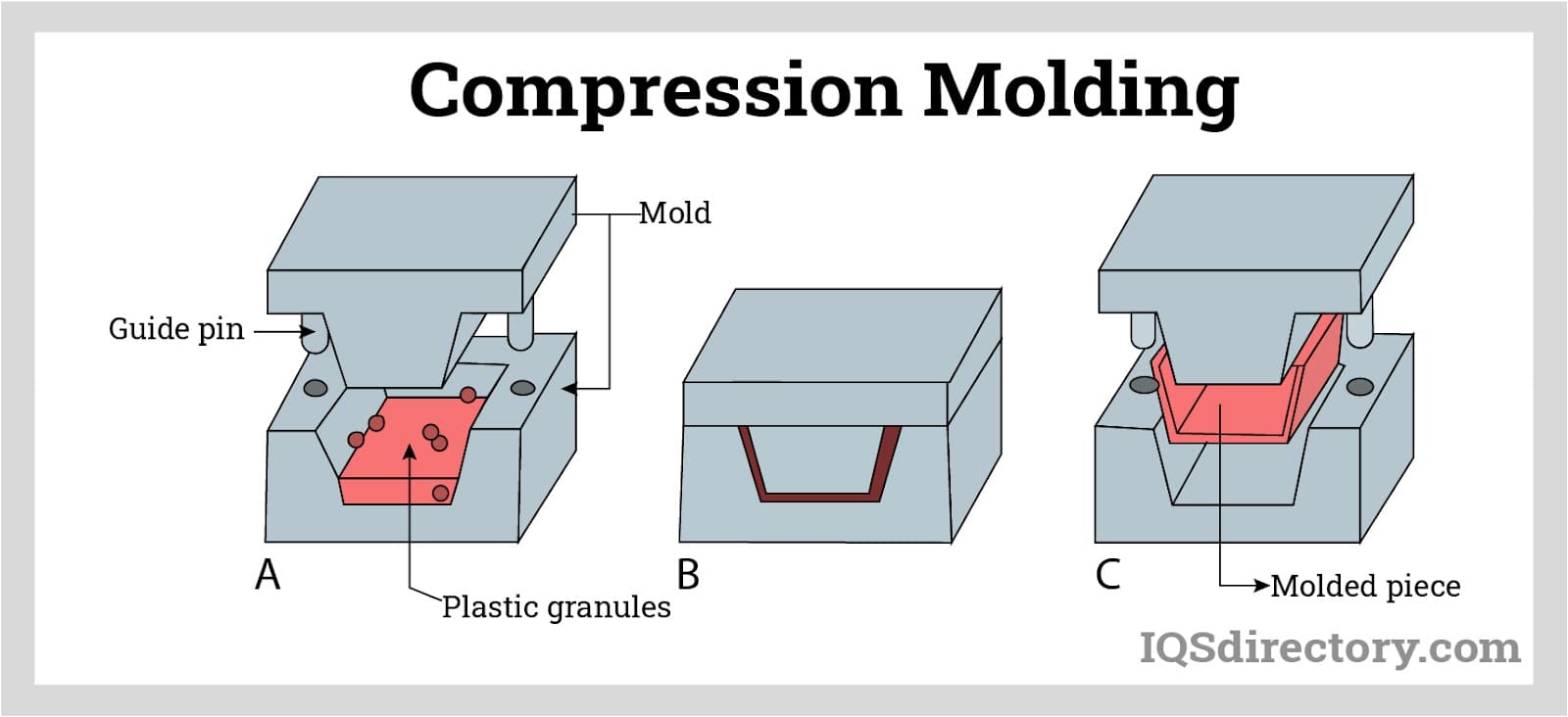
Compression Molding
Compression molding is a traditional technique where rubber and metal inserts are placed in an open mold, and pressure is applied to cure and bond the materials. While not as precise or efficient as injection or transfer molding, compression molding is cost-effective for low-volume production, large or simple parts, and prototypes. It is often used for large vibration isolation pads, custom dampers, and specialty bonded assemblies.
Key Applications of Rubber to Metal Bonded Parts
Rubber to metal bonded components are integral to countless industries and product categories. Below are some of the most common applications:
- Automotive: Engine mounts, suspension bushings, exhaust hangers, vibration isolators, brake system components, and seals.
- Aerospace: Vibration dampers, seals for landing gear, couplings, and noise isolation parts.
- Industrial Equipment: Pump and compressor seals, anti-vibration pads, conveyor rollers, and flexible couplings.
- Electronics: EMI/RFI shielding, grommets, connectors, and cable assemblies.
- Medical Devices: Seals, diaphragms, medical-grade gaskets, and instrument handles.
- Construction and Building: Expansion joints, vibration control mounts, pipe supports, and waterproof gaskets.
Have a specific application in mind? Ask our experts which rubber to metal bonding solution best fits your needs.
Benefits of Rubber to Metal Bonding
Rubber to metal bonding offers a multitude of advantages that contribute to improved product performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness:
- Reduced Assembly Complexity: By directly bonding rubber to metal substrates, manufacturers eliminate secondary fasteners and reduce the number of required parts.
- Enhanced Durability and Longevity: The bond is often stronger than the elastomer itself, resulting in assemblies that resist delamination, shearing, and environmental degradation.
- Corrosion and Chemical Resistance: The encapsulated metal is shielded from environmental exposure, extending component lifespan even in harsh or corrosive environments.
- Temperature and Weather Resistance: Properly bonded assemblies withstand wide temperature ranges, UV exposure, ozone, and moisture—critical for automotive, aerospace, and outdoor applications.
- Vibration and Noise Dampening: Rubber to metal bonded parts effectively isolate vibration and minimize noise, improving user comfort and equipment longevity.
- Customizable Performance: Engineers can tailor durometer, hardness, chemical compatibility, and geometry for specific requirements.
- Cost Savings: Fewer parts, simplified assembly, and reduced maintenance lower total cost of ownership for OEMs and end-users.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Rubber to Metal Bonding Company
Selecting the right rubber to metal bonding manufacturer is critical for the success of your project. Here are the most important factors to evaluate:
- Materials Expertise: Does the supplier offer a broad range of elastomers and metals? Are they experienced in specialty rubber formulations and surface treatments?
- Process Capabilities: Can the company provide multiple molding methods (injection, transfer, over-molding, compression) to match your design and volume needs?
- Quality Assurance: Look for suppliers with robust testing, inspection, and certification programs (ISO 9001, IATF 16949, AS9100, etc.).
- Design and Engineering Support: Does the manufacturer offer prototyping, FEA simulations, and design-for-manufacturability services?
- Production Capacity: Ensure the company can handle your required volume and lead time, whether for rapid prototyping or large-scale production.
- Certifications and Compliance: If your application is regulated (medical, aerospace, automotive), verify the supplier’s compliance with relevant standards and traceability requirements.
- Reputation and Experience: Review the company’s track record, case studies, and customer testimonials.
- Geographic Location: Consider proximity for logistics, shipping costs, and responsive service.
Looking for rubber to metal bonding manufacturers with specialized expertise? Browse our directory and request quotes from multiple suppliers to find the right partner for your needs.
How to Request a Quote or Compare Rubber to Metal Bonding Companies
To ensure the best outcome when selecting a rubber to metal bonding company, it’s wise to compare at least four suppliers using our comprehensive bonding to rubber-metal directory. Each company’s profile page highlights their core competencies, industries served, available materials, and process capabilities. Use the integrated contact form to directly request additional details or a custom quote.
Ready to take the next step? Review each company’s website to understand their specialties, then use our streamlined RFQ form to contact multiple bonding to rubber-metal companies with a single submission. This approach saves time, ensures competitive pricing, and helps you find a partner aligned with your technical and commercial requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions About Rubber to Metal Bonding
What is the strongest type of rubber to metal bond?
The strongest rubber to metal bonds are typically achieved using properly formulated adhesives, optimal surface preparation, and controlled molding conditions. Injection and transfer molding processes are renowned for producing high-strength, consistent, and durable bonds, especially when paired with appropriate elastomer and metal combinations.
Can you bond silicone rubber to metal?
Yes, silicone rubber can be effectively bonded to metal substrates using specialized primers and adhesives. Silicone bonding is popular in medical, electronics, and high-temperature applications due to its flexibility, temperature resistance, and biocompatibility. Discover more about silicone-to-metal bonding solutions.
How do I choose the right rubber to metal bonding method for my project?
The optimal bonding method depends on your part geometry, production volume, performance requirements, and budget. Injection molding is best for high-volume, precision parts, while transfer and compression molding suit lower volume or complex inserts. Over-molding and encapsulation are ideal for multi-material or specialty assemblies. Consult our technical team for personalized recommendations.
What are common failure modes in rubber to metal bonded parts?
Potential failure modes include adhesive delamination, corrosion at the interface, improper surface preparation, and elastomer degradation due to environmental exposure. Rigorous quality assurance and supplier expertise help mitigate these risks.
Can rubber to metal bonding be customized for unique requirements?
Absolutely. Leading manufacturers offer custom rubber-to-metal bonding services, including specialty elastomers, advanced adhesives, complex insert geometries, and tailored performance properties. Contact us for a custom solution.
Get Started with Your Rubber to Metal Bonding Project
Whether you need high-precision automotive bushings, durable vibration isolators, or medical-grade seals, rubber to metal bonding delivers unmatched performance, longevity, and design flexibility. By partnering with an experienced manufacturer, you can unlock the full potential of bonded assemblies for your industry and application.
Ready to request a quote or want to discuss your specific requirements? Browse our directory of rubber to metal bonding companies or contact us today for expert guidance and fast, competitive quotes.









 Rubber Extrusions
Rubber Extrusions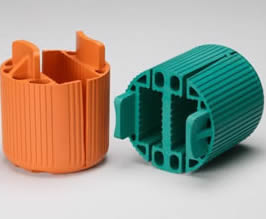 Rubber Molding
Rubber Molding Rubber to Metal Bonding
Rubber to Metal Bonding Rubber Tubing
Rubber Tubing Vibration Absorbers
Vibration Absorbers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services